CT Imaging for Acute Aortic Syndrome
Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine 2008; 75(1):7-24
Diagnostic strategy for acute aortic syndrome
Acute aortic syndrome
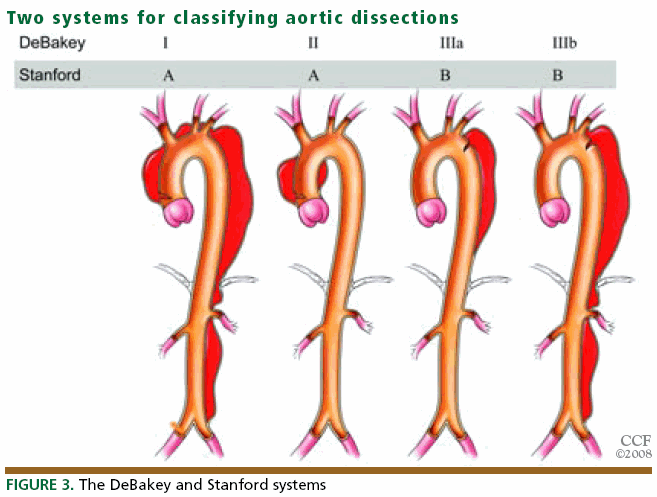
1. Acute aortic dissection
2. Intramural hematoma
Acute intramural hematoma is easily recognized in CT without contrast by the higher Hounsfield-unit value of the blood products in the wall in comparison with the flowing blood in the lumen, eccentric aortic wall-thickening and displacement of intimal calcifications.3. Penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer
4. Unstable thoracic aneurysm
An aortic aneurysm is defined as a permanent dilation at least 150% of normal size, or > 5 cm in thoracic aorta or > 3 cm in abdominal aorta.
CT signs of imminent rupture include a high-attenuating crescent in the wall of the aorta, discontinuous calcification in a circumferentially calcified aorta, an aorta that conforms to the neighboring vertebral body (“draped” aorta), and an eccentric nipple shape to the aorta.


沒有留言:
張貼留言